Introduction to Mobile Mapping
Mobile Mapping may be a correct methodology of abstraction knowledge assortment. The Mobile Mapping device mounted on a mobile platform (SUV, boat, golf cart, ATV, etc.) consists of a photographic, radar, laser, measuring instrument or any range of remote sensing systems. The mobile platform driven on a pre-planned route accumulates an abstraction model. This model consists of 3D points (point cloud) of the project space at the side of mark imaging.
Mobile mapping applications combine imaging and measuring instrument technology to acquire knowledge quickly without making physical contact, hence, reducing the chances of getting injured or exposed to hazards. The system captures physical environments through many points that area unit regenerate into 3D models that enable the specialist to investigate any structure while not having any physical contact.
Basics of Mobile Mapping
The device of the mobile mapping system collects the point cloud of all options inside a swath (a broad strip or space of something) of 250 to 300 feet all sides of the trail drive. The comparatively low power of the attention safe lasers prescribes the swath breadth. The vehicle is driven at denoted road speeds. To be helpful, this 3D model should be correct as well as dense.
After the acquisition, the abstraction model collected from the device needs to be furthermore employed within the workplace atmosphere to extract correct feature data from the point cloud. This data would thereupon embody topography, utilities, structure locations, cross sections, bridge clearances, signage, etc. Semi-automated feature extraction is equally vital to any mobile mapping project.
Up to four returns measured for every outgoing optical device pulse correspondingly permits the device to “see” through vegetation.
Mobile Mapping Positioning
GPS provides the 3D positioning of the sensors (XYZ). Inertial Navigation Systems (INS) provides the 3D rotation of the sensor (omega, phi, kappa). Distance Measurement Indicators give the distance traveled. The system can use dead reckoning for brief GPS outages due to tunnels, overhanging vegetation, etc. without significant accuracy degradation.
Configuration of Sensors
- The typical configuration includes the acquisition of LiDAR (providing 3D positional information) from two sensors (200,000 kHz Each)
- LiDAR uses a rotating laser beam as well as the GPS/INS positioning technology to measure the distance and hence the direction to objects
- Four digital cameras for imagery (5MP Each)
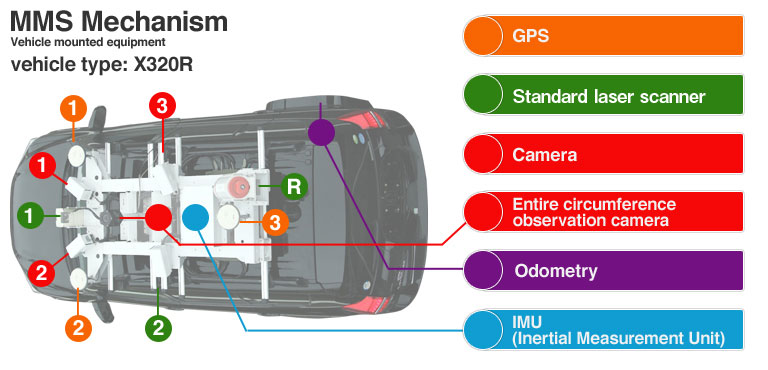
- The main components of a mobile mapping system are a GPS, standard laser scanner, digital cameras (calibrated), LiDAR sensors, odometry, IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), long distance laser, etc.
- For most applications, the vans or SUVs carry the sensors
- For rail applications, it is advantageous to mount the sensor on a Hi-Rail Vehicle.
Merits
- High operational flexibility
- Low ownership cost
- Low level of operating skills required
- High efficiency
To Summarize
Mobile mapping systems equipped with optical device scanners and digital cameras are ready with the ability and accurately to capture road signs, road facilities, utility grids, as well as vegetation. They’re an excellent means of collection of geo-data for urban designing and 3D modeling of cities with future visualization.
To know more about 3D Laser Scanning refer the blog ‘16 tips for 3D Laser Scanning, 3D Laser Scanners, and As-Built Models’
