Abstract
The influence of BIM across every life-cycle (project, realization, operations, and facility management) shows promising results and benefits. The most expansive and expensive phases of a building life cycle would be operations and facilities management. The adoption of modern asset management helps reduce the cost of building operations and maintenance, provides greater efficiency, and saves a lot of time for various building activities. A synergy of processes connecting various elements helps stakeholders build, enhance sustainability, and delay building degradation.
Introduction
The serviceable life of buildings or infrastructure is taken in an order of decades, and throughout its service, it is necessary for building stakeholders to make sure it creates habitable conditions for building tenants or users. BIM implementation is done in two ways – for new and existing buildings.
The first is implementing BIM for new structures wherein it is adopted at every lifecycle of the project – design to FM, and demolition, whilst the second part is applicable for existing buildings wherein BIM is implemented only for the maintenance phase depending on existing information, documentation, software, level of detail, etc.
Optimization of Facilities Management requires a detailed overview or information of various elements and structures, and the existing condition of a building.
The International Facility Management has defined FM as “a profession that encompasses multiple disciplines to ensure the functionality of the built environment by integrating people, place, and technology”.
Facility Management can be classified into two types viz.
Preventive Maintenance – Mitigating, diminishing, or eliminating failures before they occur
Reactive Maintenance – Reacting & solving a maintenance job after a failure has occurred
Maintenance activities can be managed and monitored through various technologies viz.
Computer-Aided Facilities Management (CAFM) – using software to plan and monitor events that lead to cost savings.
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) – a series interlinked building database that stores information on inventory, preventive maintenance, work order control, and more.
So, how is BIM data used in Facilities Management?
- Asset management and inventories
- Space management
- Systems analysis
- Environmental reasoning
- Compliance management
- Accurate information for restoration projects
Challenges in BIM implementation for Facilities Management
One of the principal challenges in the AEC industry with stakeholders using BIM for FM would be, “or is” data capture and information management during the project lifecycle. BIM can facilitate and boost data accessibility to Facilities Managers.
It is estimated that BIM can achieve more than 25% expenditure savings, and that is observed in the early operational stages of the project. The ability to link a BIM model and its consequent FM package is key for stakeholders to leverage information automation.
But, there are potential challenges that need to be addressed, and are listed as follows-
- A complete absence of best practices and guidelines due to knowledge inadequacies
- Lack of approval from owners to adopt BIM for FM in terms of cost-savings
- The construction sector does not understand Facilities Management
- Shortage of BIM skills
- The inability of Facilities Managers to pointout design deficiencies that are not maintenance friendly
- Inaccurate, incomplete, or inclusion of unnecessary information during project handover
- Interoperability issues between BIM models and FM
- A deficit of contractual framework for implementation
BIM benefits Facilities Managers, but how?
- Automate the entire data transfer process and updates – immediate and complete access to building components with 6D BIM. Cost and time savings on manual data-entry processes
- Involve Facilities Managers in the early design phases to create a greater impact on overall outcomes
- Make sense of BIM data through schedules, asset info, data management, etc.
- Enhance space management mitigates conflicts through clash detection
- Augment building maintainability through software and information supply
- Create maintenance activities or programs based on historical trends viz. service history, contract info, and specifications
- Diminish environmental impacts through sustainability and efficient energy implementation
Asking the right questions to setup a robust BIM for FM staging platform
- What kind of data do you want to control?
- What kind of processes or technology are you using to manage your data and facility?
- What are the systems in place?
- Do your Facilities Management teams have the knowledge and skill-set to manage?
- How much of your building or infrastructure is new or existing?
- What is your goal to operate tomorrow?
The most efficient BIM for FM process structure
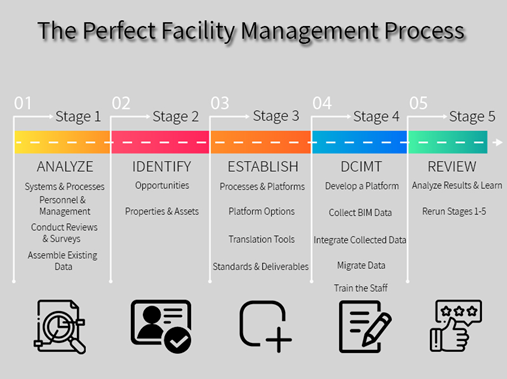
Here is a list of the top 5 Facilities Management Trends of 2019 & beyond
Biometric systems – verify a person’s identity based on exclusive characteristics
Applications or devices – fingerprints, facial, or retinal recognition
Hands-free or wearable technology – implementing smart-wearable tech has made Facilities Management secure and safe through data collection and analysis
Applications or devices – RFID technology, sensors, etc.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) – 3-dimensional interactive models based on various processes, object libraries, HVAC components, lighting, electrical systems, product specifications, and more
Applications or devices – 3D modeling software, cloud-based software to integrate design and construction models, smartphones or tablets
Autonomous systems – using the Internet of Things orrfi(IoT) to build smart buildings increases efficiency, saves energy, and collects vital data on space metrics. All these connect and communicate together using smart sensors or autonomous systems.
Applications or devices – temperature and humidity sensors to maintain environmental conditions, listening and vibration sensors to manage and monitor failures and performance
Drones and LIDAR technology – drones and LIDAR technology are used by Facilities Managers to view building and ground assets. LIDAR is used to collect precise information and convert it into highly visual 3D models of building surfaces, terrain, elevation, and more.
Applications or devices – LIDAR sensors or devices, drones, software
Key Takeaways
The overall purpose of using BIM for Facilities Management or FM would be to facilitate healthy, safe, efficient, and effective environments for building users. Stakeholders can use this data through various project phases viz. Projects, Operations, Maintenance, & Restoration. Using BIM for FM reduces the cost and time required, and enhances customer satisfaction through operations and facility management.
BIM for FM is an ideal process and technology that most of the stakeholder’s desire, but it is rarely used as it is quite overwhelming for some. However, there are proven case studies and projects that help AEC professionals and stakeholders understand its significance to optimize facilities.
Contact Us: – 703-994-4242
Visit us: – www.bimengus.com

